The global offshore wind power installed capacity is experiencing rapid growth. According to the statistics of the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), the global offshore wind power installed capacity will increase by 6.1GW in 2019. According to the statistical results of the Wind Energy Professional Committee (CWEA) of the China Renewable Energy Association, 588 new offshore wind power installations and 2.49GW of new installed capacity were added in China, an increase of 50.9% year on year. With the growth of offshore wind power installed capacity, the demand for offshore wind power operation and maintenance has also increased. Offshore wind turbines have been in a harsh marine environment for a long time. In terms of unit failure rate, offshore wind power is significantly higher than onshore wind power. In addition, more complex natural conditions also bring more challenges to the operation and maintenance of offshore wind power. The construction of smart offshore wind farms in the future depends on good operation and maintenance management, which requires the support of scientific operation and maintenance strategies, intelligent fault diagnosis and monitoring technology, and stable and efficient operation and maintenance ships and other equipment.

1、 Development and characteristics of offshore wind power
At present, in response to global climate change, major economies have set carbon neutral targets. Carbon emission reduction has driven the accelerated transformation of the global energy structure, moving forward from the era of fossil energy to the era of renewable energy. The energy revolution has ushered in new development opportunities for the wind power industry.
Since Denmark put the world's first offshore wind farm, Vindeby, into operation in 1991, offshore wind power has entered the road of rapid development. Compared with onshore wind power, offshore wind power resources are more abundant. Offshore wind power units do not need to occupy land resources, are closer to the power load center, and have higher utilization hours of power generation. In the context of the rapid development of the wind power industry, the development speed of offshore wind power is even faster than the industry as a whole.
Offshore wind turbines are developing towards large-scale, and the cost of levelized kilowatt-hour power is decreasing. Fans with larger impeller diameter and larger power can provide greater annual power generation, thus reducing costs. The research and development of high-power wind turbines by domestic and foreign machine manufacturers is ongoing. Vestas released the world's first 10MW wind turbine in September 2018; In November 2019, the first prototype of GE12 MWHailiade-X direct-driven fan was installed and tested in Rotterdam, the Netherlands; In May 2020, Siemens Gomesa released the SG14-222 direct-drive fan, which is expected to be put into commercial use in 2024, with a maximum power of 15MW. On the other hand, the construction site of offshore wind power is developing towards deeper water depth and farther offshore sea areas, and the number of floating wind turbines is increasing, which also means that the operation and maintenance environment will be worse and the maintenance difficulty will increase.
China's offshore wind power shows a trend of scale, intelligence, customization and large-scale development. In the future, China will build more million-kilowatt or ten-million-kilowatt offshore wind farms, form the advantage of intensive development, and strive to achieve parity at the end of the "14th Five-Year Plan". The smart wind farm will be equipped with intelligent technology, which can realize health perception, fault detection, cluster intelligence and other functions; The complete machine, tower foundation, drive chain, blades and yaw system and other subsystems have independent intelligent application expansion; The smart wind farm will integrate the big data platform architecture, algorithms and models to build the power Internet of Things platform. Guided by the cost of kilowatt-hour electricity, offshore wind power will tend to be developed in a customized way, increase the power on the grid, improve economic efficiency, control the construction cost and reduce the operation and maintenance costs. More high-power offshore wind turbines of more than 10 MW will be put into operation, and the power generation capacity will be further improved.
The development of offshore wind power is changing with each passing day. Large-scale wind turbines, deep-water offshore layout and the use of floating wind turbines pose new challenges to the operation and maintenance of offshore wind power. Future smart offshore wind farms need the support of intelligent and efficient operation and maintenance.
2、 Current situation and difficulties of offshore wind power operation and maintenance market
The existing operation and maintenance data show that under the same installed capacity, the operation and maintenance cost of offshore wind power is more than twice that of onshore wind power, and the operation and maintenance cost of offshore wind power accounts for more than 1/4 of its cost per kilowatt hour. Most of China's offshore wind farms have a service life of 25 years. After the offshore wind turbines are connected to the grid for power generation, the manufacturer of the complete machine will provide a 5-year warranty service. Outside the warranty period, the operation and maintenance work of wind turbine units shall be undertaken by the wind farm investor or the third party operation and maintenance service provider.
As shown in Figure 1, the cost of offshore wind power operation and maintenance mainly includes wind turbine operation and maintenance, operation and maintenance ship maintenance and insurance. Due to the cost consideration of the investor and the "price war" between the suppliers of the complete machine, the purchase price of the offshore wind turbine is falling continuously, which also leads to the use of more cheap parts, reducing the configuration of the complete machine, and making it difficult to guarantee the quality of the wind turbine. High unit failure rate and large maintenance workload are the biggest difficulties in offshore wind power operation and maintenance.

Figure 1 Operation and maintenance costs of offshore wind power
Many domestic offshore wind farms use the modified onshore wind turbines instead of the original offshore wind turbines. The modified onshore wind turbine is difficult to adapt to the complex conditions at sea for a long time, and is more prone to failure. Due to the influence of tide and other conditions, the operation and maintenance of offshore wind power is restricted by the window period, and the accessibility of offshore wind turbines is poor. The adverse weather conditions and bad sea conditions limit the duration of maintenance operations, and also bring greater safety risks.
China lacks mature experience in the field of offshore wind power operation and maintenance. The current operation and maintenance methods are mainly based on the use of onshore wind power, that is, the operation and maintenance strategy of planned maintenance, supplemented by fault maintenance. This operation and maintenance mode can not well adapt to the operation characteristics of offshore wind power. In terms of troubleshooting of offshore wind power, the maritime traffic of operation and maintenance personnel is greatly affected by the sea conditions. Large uncertainty may cause long-term shutdown of the unit and seriously affect the production efficiency of the wind farm. The key issues to be solved in the field of offshore wind power operation and maintenance mainly include:
(1) Improve the operation status monitoring system of offshore wind turbine, use the unit health diagnosis technology to realize the unit abnormal identification and predict the unit life.
(2) Further optimize the maintenance strategy of offshore wind farms, standardize the operation and maintenance mode, optimize the operation and maintenance resource management plan, and reasonably allocate various operation and maintenance resources. The formulation of the operation and maintenance strategy should be combined with the reliability data of the unit to improve the efficiency of the single sea trip as much as possible, so as to avoid frequent sea trips and save the operation and maintenance costs.
(3) The unit with fault-tolerant operation capability can still work stably for a certain period of time after partial failure. In the case that the fault of offshore wind turbine is unavoidable, the fault-tolerant operation function of the unit has important research value.
(4) Carry out the correlation study of multi-component faults of offshore wind turbines, and analyze the correlation of functions and structures between multi-components of multi-units.
3、 Innovation trend of offshore wind power operation and maintenance technology
The rapid development of offshore wind power has put forward new requirements for the operation and maintenance work. The innovation of offshore wind power operation and maintenance includes changing the operation and maintenance mode, optimizing the operation and maintenance strategy, improving the operation and maintenance equipment, improving the fault diagnosis and monitoring technology, etc. The intelligent operation and maintenance system of offshore wind power includes a number of intelligent technologies, which realize intelligent perception through intelligent sensing technology, edge computing technology and robot technology; Realize intelligent monitoring through data visualization technology, 3D modeling technology and network security technology; Intelligent analysis is realized through pattern recognition technology, fault early warning technology and big data technology; Make intelligent decisions with the help of expert knowledge base, artificial intelligence technology and digital twin technology; Intelligent assistance is realized through mobile internet technology, virtual reality technology and augmented reality technology.
1. Offshore wind power operation and maintenance management technology
The intellectualization of the whole life cycle of offshore wind power is the key to achieve the optimal cost of offshore wind level standardization. The intelligent operation and maintenance of offshore wind power is a systematic project.
Intelligent operation and maintenance system uses big data and intelligent data technology to make operation and maintenance decisions based on data. Adopt sophisticated cost control, improve the refinement level of operation and maintenance management and effectively reduce the operation and maintenance costs through real-time calculation of fan operation and maintenance costs and benefits throughout the life cycle. Do a good job in the offshore test of wind turbine components, build the "genetic engineering" of offshore wind power, formulate a reasonable operation and maintenance plan, and improve the reliability of unit operation. According to the early warning information of large parts, lock the lifting vessels and spare parts of large parts in the area in advance to shorten the downtime of large parts. Through the integrated system of fault warning and operation, inspection and maintenance, optimize the operation and maintenance plan and operation and maintenance scheduling, and reduce the operation and maintenance costs of offshore wind power. Evaluate the power generation performance and power loss reasons of offshore wind farms, carry out the research and application of control strategy optimization technology, and further improve the power generation of wind turbines. Optimize the regional wind farm transportation tools of different sea areas and different scales, improve the operation and maintenance efficiency, and reduce the daily operation and maintenance transportation costs.
It is the development goal of the offshore wind power operation and maintenance mode to scientifically and reasonably plan the operation and maintenance time and route, adopt the pre-operation and maintenance mode to eliminate the hidden trouble and reduce the operation and maintenance cost. For the planning of the operation and maintenance route, the safe, convenient and cost-effective operation and maintenance transportation route should be selected based on the wind power prediction, the accessibility of the operation and maintenance ships, the unit operation status and health status.
Risk-based maintenance can reduce the overall maintenance difficulty and life cycle cost, and present the availability and unit performance that are satisfactory to all parties. Planned maintenance combined with the traditional operation and maintenance strategy of fault maintenance consumes a lot of manpower, material and financial resources. With the continuous progress of operation and maintenance technology, the operation and maintenance strategy based on condition-based maintenance has become the development trend.
Condition-based maintenance takes the equipment status as the starting point, finds latent faults and evaluates the equipment status through online monitoring and offline measurement. Condition-based maintenance is highly targeted. Through comprehensive analysis of the equipment, it can determine whether to repair the equipment, and the maintenance effect is also better. The operation and maintenance strategy based on condition-based maintenance can facilitate the unified scheduling of operation and maintenance resources to carry out the maintenance of multiple units, improve the efficiency of a single trip to sea, reduce the number of trips to sea, and reduce transportation costs. Condition-based maintenance is a major innovation in the operation and maintenance management of offshore wind power. The realization of condition-based maintenance needs to monitor and analyze the operation status of units, strengthen the life cycle monitoring of components and the condition monitoring of large components in combination with the characteristics of different offshore wind farms.
2. Monitoring and analysis technology of offshore wind turbine
The intelligent monitoring of offshore wind power includes underwater intelligent monitoring, structural fatigue and damage monitoring, submarine cable monitoring and foundation scouring monitoring. Intelligent analysis technology covers weather forecast and early warning system, window period management system, ship, route, personnel management system and maritime security system. The online monitoring technology transmits and visualizes the observation data in real time through a variety of communication media, providing convenience for data processing. Underwater intelligent monitoring uses the underwater robot to inspect the underwater part of the target unit, and can visually monitor the overall state of the foundation. For the fatigue and damage monitoring of the supporting structure, the deformation, stress, displacement, vibration and corrosion status of the structure are monitored by sensors and transmitted to the monitoring system in real time. The specific monitoring items and the location of monitoring points can be selected according to the specific operation, maintenance and safety assessment requirements of the wind farm. The monitoring of marine environmental parameters obtains the project sea area data in real time through sensors and high-speed transmission technology, including wave data, wind data, ocean current data, temperature and salinity data, and accumulates background parameter data for the operation and maintenance of offshore wind power. Submarine cable monitoring is usually based on the cable online monitoring method of optical fiber and partial discharge to safely monitor the operation status of submarine cables.
Sea area monitoring can reduce cable damage caused by ship anchoring by continuously monitoring the passing ships in the sea area around the submarine cable. The foundation scour monitoring can obtain parameters such as scour depth through data acquisition equipment, which can be combined with the support structure response monitoring to provide higher security for offshore wind power infrastructure.
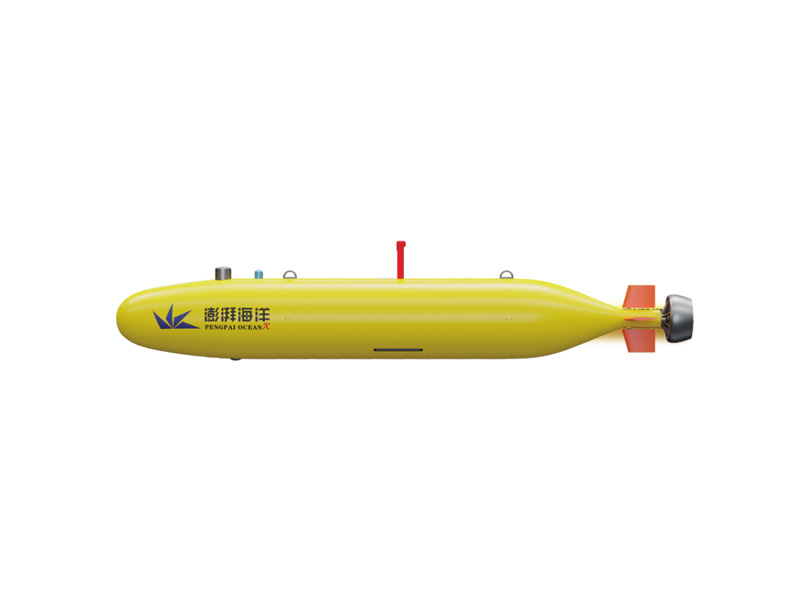
3. New wind power operation and maintenance ship
The intelligent monitoring of offshore wind power includes underwater intelligent monitoring, structural fatigue and damage monitoring, submarine cable monitoring and foundation scouring monitoring. Intelligent analysis technology covers weather forecast and early warning system, window period management system, ship, route, personnel management system and maritime security system. The online monitoring technology transmits and visualizes the observation data in real time through a variety of communication media, providing convenience for data processing.
Underwater intelligent monitoring uses the underwater robot to inspect the underwater part of the target unit, and can visually monitor the overall state of the foundation. For the fatigue and damage monitoring of the supporting structure, the deformation, stress, displacement, vibration and corrosion status of the structure are monitored by sensors and transmitted to the monitoring system in real time. The specific monitoring items and the location of monitoring points can be selected according to the specific operation, maintenance and safety assessment requirements of the wind farm. The monitoring of marine environmental parameters obtains the project sea area data in real time through sensors and high-speed transmission technology, including wave data, wind data, ocean current data, temperature and salinity data, and accumulates background parameter data for the operation and maintenance of offshore wind power.
Submarine cable monitoring is usually based on the cable online monitoring method of optical fiber and partial discharge to safely monitor the operation status of submarine cables. Sea area monitoring can reduce cable damage caused by ship anchoring by continuously monitoring the passing ships in the sea area around the submarine cable. The foundation scour monitoring can obtain parameters such as scour depth through data acquisition equipment, which can be combined with the support structure response monitoring to provide higher security for offshore wind power infrastructure.
At present, more than 400 wind power operation and maintenance ships have been put into use in the world. The new offshore wind power operation and maintenance ships are larger in size, can carry more instruments, equipment and parts, and have good riding comfort, faster speed, higher safety of personnel transfer, and stronger resistance to wind and waves. There are many types of professional wind power operation and maintenance ships, and the specially designed bow can not only allow the operation and maintenance personnel to climb the ladder from the bottom of the wind turbine to land, but also reduce the sway of the hull. The main types of wind power operation and maintenance ships include monohull, catamaran, trimaran, small waterplane catamaran, surface effect ship and small waterplane trimaran, etc. The typical parameters of various types of operation and maintenance ships are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Typical parameters of different types of operation and maintenance ships

According to the characteristics of offshore wind power projects in different sea areas in China, different forms of operation and maintenance ships are selected. Most of the coastal projects in Jiangsu are located in the tidal zone waters, with the operating water level of 0~20m, wind speed of 3 m/s~7 m/s, wave height of 0.5 m~4.6 m. The offshore distance of the completed wind farm is 3 km~50 km, and the average wave period of 3.1 s. This sea area is suitable for the use of catamarans, small water plane catamarans and residential boats. The coastal waters of Fujian, Guangdong and Zhejiang are characterized by complex and changeable sea conditions, many islands and reefs, large swells, rapid water flow, large wind waves, water depth of 10m~50m, annual average wind speed of 8.0m/s, and average wave height of 2.0m. The offshore distance of the built wind farms is 3km~30km. The offshore project of this sea area is relatively close, and small water-plane catamaran, surface effect ship and small water-plane trimaran with strong wind and wave resistance and fast speed can be selected. The sea conditions in the Bohai Sea and the North Yellow Sea are better than those in the windy Fujian and Jiangsu coastal areas in the tidal zone. However, sea ice will occur in the sea area in winter. The operation and maintenance ships need to add the enhanced ice-breaking device in the Class B ice zone at the bow, and add the warm and antifreeze equipment. Figure 2 shows the "Xiongcheng Tianwei 1" catamaran operation and maintenance ship delivered on July 18, 2020. The ship is equipped with advanced low-voltage DC integrated power technology for ships, which is the first application of this technology in the field of civil ships.

Figure 2 "Xiongcheng Tianwei 1" wind power operation and maintenance ship
In addition to conventional O&M ships, the O&M mother ship is a new development trend. The typical mother ship can accommodate more than 40 people, can carry parts, has a self-sustaining force of more than 1 month, has excellent berthing performance, and is equipped with wave compensation ladder and dynamic positioning system. However, its cost and operating cost are relatively high, and its application is relatively small at present. Figure 3 shows the "WindeaLeibniz" O&M mother ship built by Uzbekistan