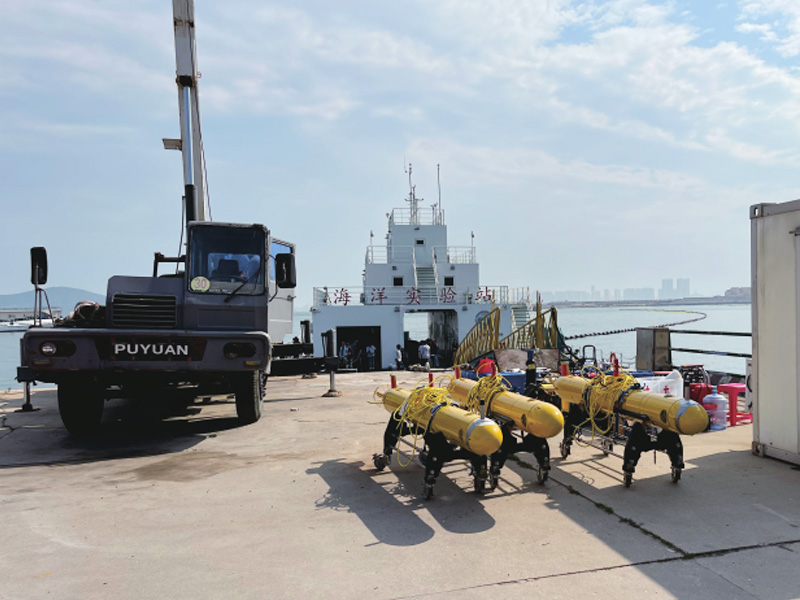
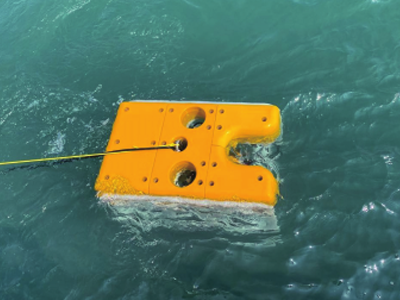
"70% of the earth's surface is the ocean, but the ocean environment is very bad, and human cognitive means are extremely limited. For example, 'ask for resources from the ocean'. In fact, our energy development is mainly at a depth of more than 300 meters. If we want to dive, the means are seriously insufficient." Yu Haibin, director of the Shenyang Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said at the summit forum on artificial intelligence and underwater robots held on September 3, Underwater robot is an important equipment for exploring the ocean. It has great potential in ocean observation, exploration and underwater extreme environmental operations. In particular, deep sea salvage, trench scientific research and sample sampling. Yu Haibin said that since the 1960s, research on manned submersibles, wired remote-controlled underwater vehicles and autonomous underwater vehicles has been carried out successively. At present, it has entered the era of intelligent underwater robot
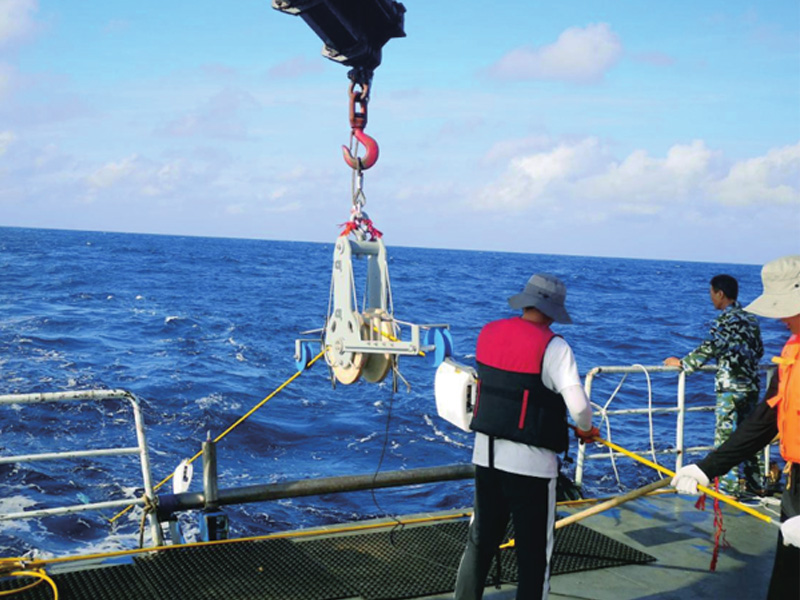
It is not easy to build robots to fly in the air and run on the ground. It is more difficult to swim in the water. Compared with land and airspace, the seabed environment is much more complex. It has higher capabilities for robot navigation, obstacle avoidance, recognition, detection, tracking, formation and combat. "Every time I do an experiment, I can't sleep. The underwater robot experiment often lasts for dozens of hours. I'm afraid to wait on the ship. I don't know whether the machine is safe or whether it can come back." Yu Haibin's mood reflects the difficulty of intelligent control of the underwater robot. According to Wang Tianmiao, honorary director of the Aerospace Robotics Research Institute of Peking University, the traditional navigation methods of underwater robots include dead reckoning, inertial navigation and Doppler sonar navigation. However, these methods will have a large cumulative error after long distance navigation. At present, the integrated navigation adopted by most underwater robots has effectively improved the navigation accuracy, but the error still exists. "Machine loss" occurs from time to time. How to find a new navigation mode is the focus of the study. When the robot enters the water, it needs to communicate with other devices. Underwater acoustic communication is the main means of underwater communication. Underwater laser communication, which is being developed all over the world, still has a long way to go before its application.

Gao Wen, an academician of the CAE Member, said that he hoped that the intelligent system would have faster processing speed, higher precision, clearer conclusions and more effective energy consumption. Energy consumption is directly related to the endurance of underwater robots. "People's daily energy consumption is equivalent to a 20 watt light bulb. A little food can be used to listen, read and write. A human-like recognition system requires tens of thousands of times of energy consumption, which is equivalent to a primitive and widely designed supercomputer."
In addition, at present, most underwater robots carry heavy hydraulic rigid manipulators and grippers, which have great defects in underwater biological sampling, archaeological exploration and salvage of valuables. At the scene, Wang Tianmiao showed a software manipulator that mimics the tentacles of octopus. "The application of intelligent materials and bionic structures is a breakthrough point for robot safety, dexterity, adaptability to environment and objects," said Wang Tianmiao. Inspired by natural underwater organisms, it helps researchers explore the new structure of underwater autonomous manipulators, and realize the fine operation and flexible grasping of the manipulator based on tactile and force feedback
The biomimetic fish, the dolphins and octopus tentacles displayed on the scene are different from the robots in general impression, but Tan Min, a researcher at the Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, stressed that "although it is still very elementary, it is not playing". According to him, they developed a bionic dolphin robot for water quality monitoring based on killer whales, which can carry different water quality sensors to achieve water quality monitoring tasks, and found the basic civil applications of underwater robots. "We have successfully collected online the important water quality parameters of the reservoir, such as pH, conductivity, temperature and depth, at the Qinghai Naked Carp Research Center and Yushu Zhangshu Reservoir. The successful implementation of the dynamic water quality monitoring experiment based on the bionic robot dolphin not only provides new technical means for the protection of the three river sources, but also provides new technical means for the dynamic independent water quality monitoring. "Tan Min said that in the future, there may be similar applications in the detection of corrosion degree of offshore oil platforms and underwater pollution monitoring of dams.